Abstract
BACKGROUND:
In recent years, CAR-T cell therapy has rapidly developed and benefits a lot to patients with B-cell hematologic malignancy. Whereas, all marketing CAR-T products are manufactured using virus which increase the tumorigenesis risk and cost in time and labor for clinical application. Here, we evaluated the safety and efficacy of a virus free CAR-T cells (BRL-201) which PD1 locus were specifically integrated with anti-CD19 CAR sequence through CRISPR/Cas9 in treating adult patients with relapsed/refractory (r/r) B-NHL (NCT04213469).
METHODS: This single-arm phase I dose escalation clinical trial evaluates BRL-201 in adult patients with r/r B-NHL. Adult patients with r/r B-NHL underwent leukapheresis and a lymphodepletion chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide (500mg/m2 , D -3 to -2) and fludarabine (30mg/m2, D -4 to -2) before BRL-201 infusion. Dose escalation are based on 3+3 escalation rule, including three cohorts: 2×106/kg, 4×106/kg, 6×106/kg. The primary endpoint was the incidence of dose-limiting toxicities. The secondary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving an objective response (i.e., the combined proportion of participants who had a complete or partial response) at 3 months as per investigator's assessment.
RESULTS: Between May 3, 2020 and August 10, 2021, 25 patients with r/r B-NHL were enrolled and 21 received BRL-201 with a median age of 56 years (range, 34-70) and a median of 4 (range, 1-9) prior lines of therapy. Among all the treated patients, 17 patients (93.8%) were diagnosed with disease stage III or IV, and 13 patients (81.3%) were assessed with high-intermediate to high risk according to IPI or aaIPI score assessment. Two patients had undergone autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) and one patient had a history of primary refractory disease. Of 8 patients with pretreatment tumor samples PD-L1 expression detection, 2 (25%) had a high level (≥80% )PD-L1 expression,2 (25%) had a medium PD-L1 expression (≥10% ).
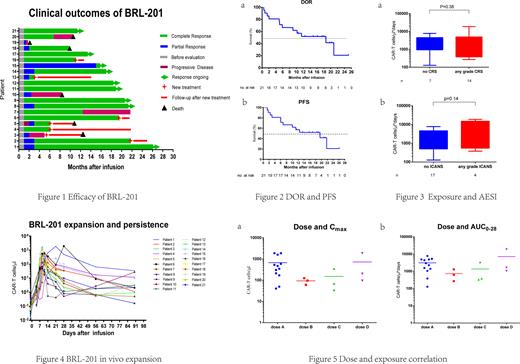
As of July 19, 2022, 21 assessable patients in phase 1 were followed up for a median of 12 months (1-26m). According to investigator's assessment, all of 21 (100%) patients had an objective response to BRL-201 and 18 (85.7%) patients had a complete response (CR) as best response (Fig. 1). Seventeen of 21 (80.9%) patients had an ongoing objective response at 3 months, 16 of 21(76.2%) patients had a CR and 1 of 21 (4.8%) patients had a partial response. One of the two patients with a high level (≥80% ) PD-L1 expression achieved CR and still remained CR at 26 months after infusion. The median duration of response for all 21 patients was 18.6 months (Fig. 2a). The median progression free survival was 19.5 months (Fig. 2b). Fourteen patients (66.7%) experienced low grade (1 or 2) cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and only one patient received tocilizumab. Four patients (19.0%) experienced immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) which was grade 1 or 2. No correlation was found between BRL-201 exposure (area under curve, AUC0-28) and the incidence of CRS/ICANS (Fig. 3). The peak of BRL-201 was observed at the median time of 11 days after infusion, which reached a median level of 211.9 (34.8-1880.0) CAR+ cells/µL in peripheral blood (Fig. 4). There was no correlation between dose and exposure (Fig. 5).
CONCLUSIONS: This is a first-in-human study of a novel type of non-viral genome specific targeted CAR-T cells in treating r/r B-NHL. As a two-in-one approach without using virus, the manufacturing procedure is simplified, with shortened preparation time, reduced production expenses. Low incidence and mild grade of CRS/ICANS preliminarily showed the high safety of BRL-201. The high efficacy of BRL-201 in r/r B-NHL was also observed, with a best of response (BOR) of 100% and an ORR of 80.9% at 3 months.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal